

Thoracic surgery refers to any procedure performed in the chest (thorax) area, including critical organs such as the lungs, heart, oesophagus, trachea, diaphragm, and chest wall (ribs, breastbone, and muscles). This specialized field includes a range of surgeries that treat various diseases and conditions affecting the chest cavity. Thoracic surgeons treat both benign (non-cancerous) and malignant (cancerous) diseases, as well as conditions caused by trauma, infection, or congenital issues.
Some of the most common procedures in thoracic surgery include:
Thoracic surgery can be performed using two main approaches:

Thoracic surgeons are skilled in treating a wide variety of conditions that affect the chest, lungs, and surrounding areas, including:
Thoracic surgery is one of the most intricate fields of surgery. Its breadth is vast, and the techniques employed are highly specialized. Thoracic surgeons work alongside other specialists, such as pulmonologists, oncologists, cardiologists, and gastroenterologists, to provide a comprehensive treatment plan for patients with complex thoracic conditions.
Thoracic surgeons are highly skilled specialists in managing diseases and conditions that affect the chest area, including the lungs, heart, oesophagus, and surrounding structures. Their expertise in open and minimally invasive procedures is essential for treating severe conditions like lung cancer, heart disease, and respiratory disorders. Consulting a thoracic surgeon ensures patients receive the best care tailored to their needs.
Understanding what to expect during your journey with thoracic surgery can reduce stress and help you make informed decisions about your care.
Thoracic surgery encompasses a wide variety of operations to address severe conditions in the chest, lungs, heart, and surrounding structures. These procedures can be life-saving or crucial for improving a patient's quality of life, particularly in cases where medical treatments alone are insufficient. Below are some common thoracic surgeries, each designed to treat specific conditions.
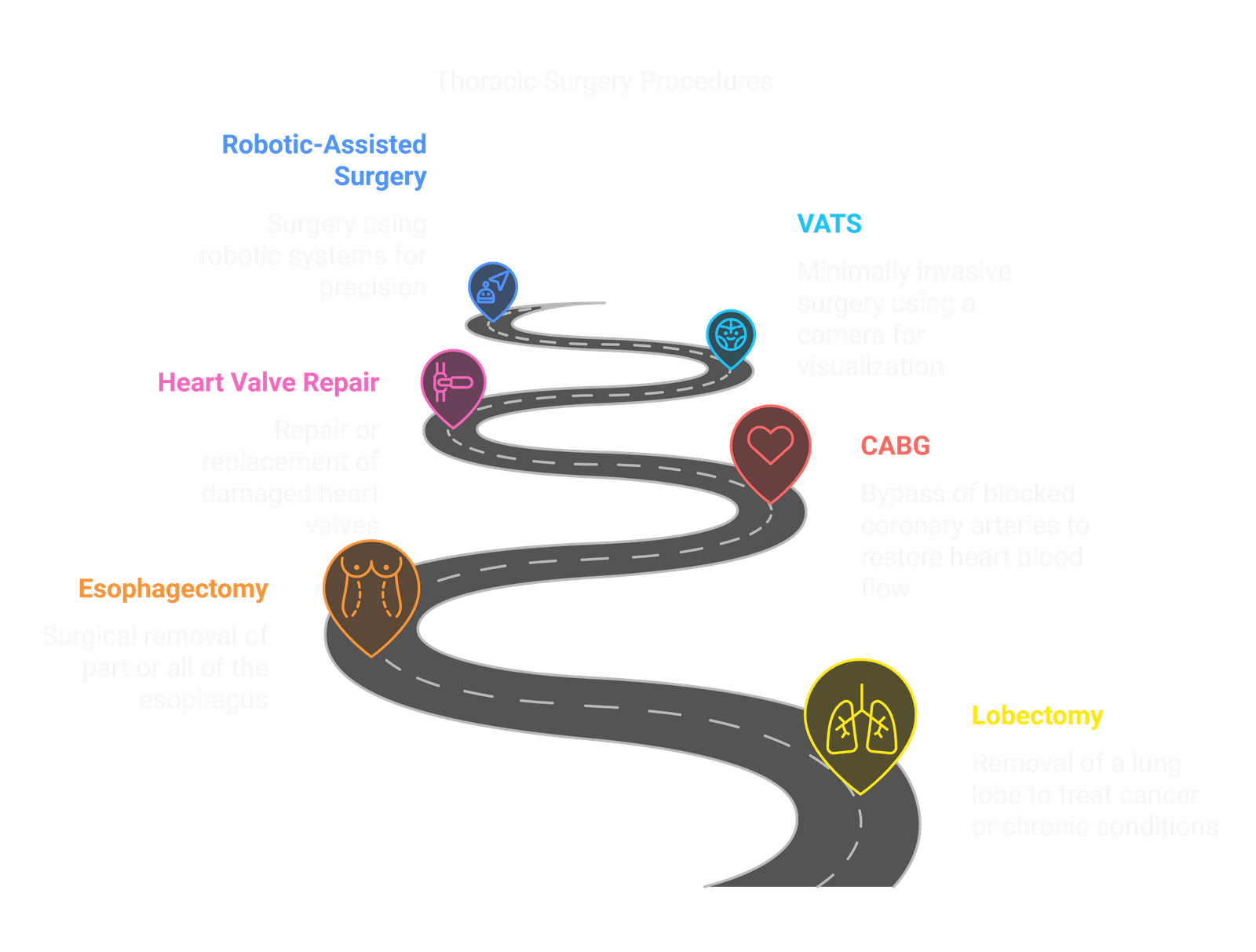
Lobectomy involves the surgical removal of a portion (lobe) of the lung and is most commonly performed in the treatment of lung cancer. In patients with localized lung tumours, removing the affected lobe can prevent the spread of cancer and significantly increase the chances of survival. Lobectomy may also be used to treat chronic conditions such as emphysema, lung infections, or benign lung tumours.
Esophagectomy is the removal of part or all of the oesophagus, typically done for oesophagal cancer, Barrett's oesophagus, or severe GERD causing significant damage or pre-cancerous changes.
Heart surgeries include a wide range of procedures to treat diseases and abnormalities affecting the heart. Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG) and heart valve repair/replacement are the most common procedures thoracic surgeons perform.
Minimally invasive thoracic surgeries, such as Video-Assisted Thoracic Surgery (VATS) and robotic-assisted surgery, are becoming increasingly common due to their numerous advantages over traditional open surgery. These procedures involve smaller incisions, reduced pain, and shorter recovery times, making them especially beneficial for patients seeking quicker recovery and less disruption to their daily lives.
These procedures are tailored to the patient's needs, considering the severity of the condition and the best surgical method for treatment. Surgeons in India are increasingly skilled in performing traditional and minimally invasive surgeries, offering patients advanced treatment options. Whether treating lung cancer, heart disease, or oesophagal conditions, thoracic surgeons customize each surgery to ensure the best possible outcome for the patient. With technological advances, these procedures are more accessible and efficient than ever, making thoracic surgery a critical part of modern medical care.
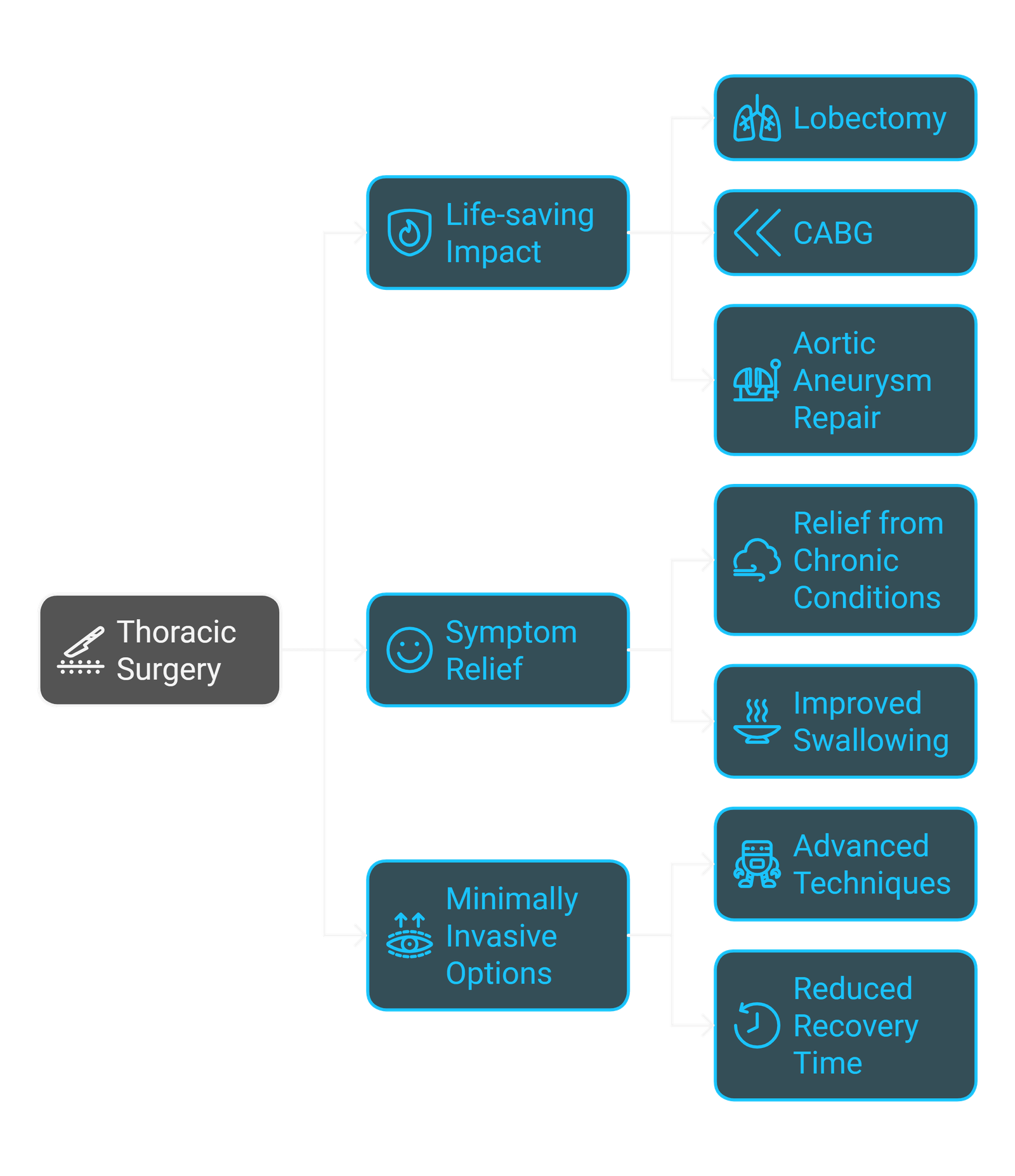
Life-saving Impact: Thoracic surgery can significantly enhance survival chances for life-threatening conditions like lung cancer, heart disease, and aneurysms. For example, surgeries like lobectomy (removal of part of the lung) can effectively remove tumours in lung cancer patients, preventing the spread of cancer to other parts of the body.
Coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) restores blood flow to the heart by bypassing blocked arteries, preventing heart attacks and long-term complications. For patients with life-threatening conditions, thoracic surgery often offers a survival pathway and a chance to live a longer, healthier life.
In the case of aortic aneurysms, surgical repair can prevent rupture, which could be fatal without intervention. By addressing these serious medical issues head-on, thoracic surgery often serves as a crucial and potentially life-saving intervention.
Symptom Relief: Thoracic surgery saves lives and dramatically improves quality of life by relieving painful symptoms. Thoracic surgery saves lives and profoundly enhances a patient's quality of life by effectively relieving painful or debilitating symptoms. Many patients with chronic lung conditions, such as emphysema or COPD, find relief from persistent shortness of breath or recurring lung infections after undergoing procedures like lobectomies or lung volume reduction surgery. Similarly, surgeries for conditions like oesophagal cancer or gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) can eliminate symptoms like severe dysphagia (difficulty swallowing), acid reflux, and chronic heartburn, enabling patients to eat and breathe more easily.
For patients with swallowing difficulties caused by oesophagal narrowing or tumours, an esophagectomy (removal of part or all of the oesophagus) can provide lasting relief, reducing discomfort and improving their ability to consume food and fluids. Ultimately, thoracic surgery restores normal bodily functions, helping patients regain a sense of normalcy and comfort in their daily lives.
Minimally Invasive Options: Recent advancements in minimally invasive techniques, including Video-Assisted Thoracic Surgery (VATS) and robotic-assisted surgery, have greatly enhanced patient outcomes. These procedures typically involve smaller incisions, less blood loss, and reduced trauma to surrounding tissues. The benefits of these techniques extend to faster recovery times, reduced pain, and shorter hospital stays. Because the incisions are smaller, patients experience less scarring and can resume their normal activities more quickly. This is particularly important for older adults or patients with pre-existing conditions who may be at higher risk for complications from more invasive procedures.
Moreover, minimally invasive procedures have a lower risk of complications like wound infections or delayed healing, making them a preferable option for many patients, especially when treating the condition allows such approaches. Surgeons in India are increasingly adopting these advanced methods, ensuring that patients receive high-quality care while minimizing recovery time and discomfort.
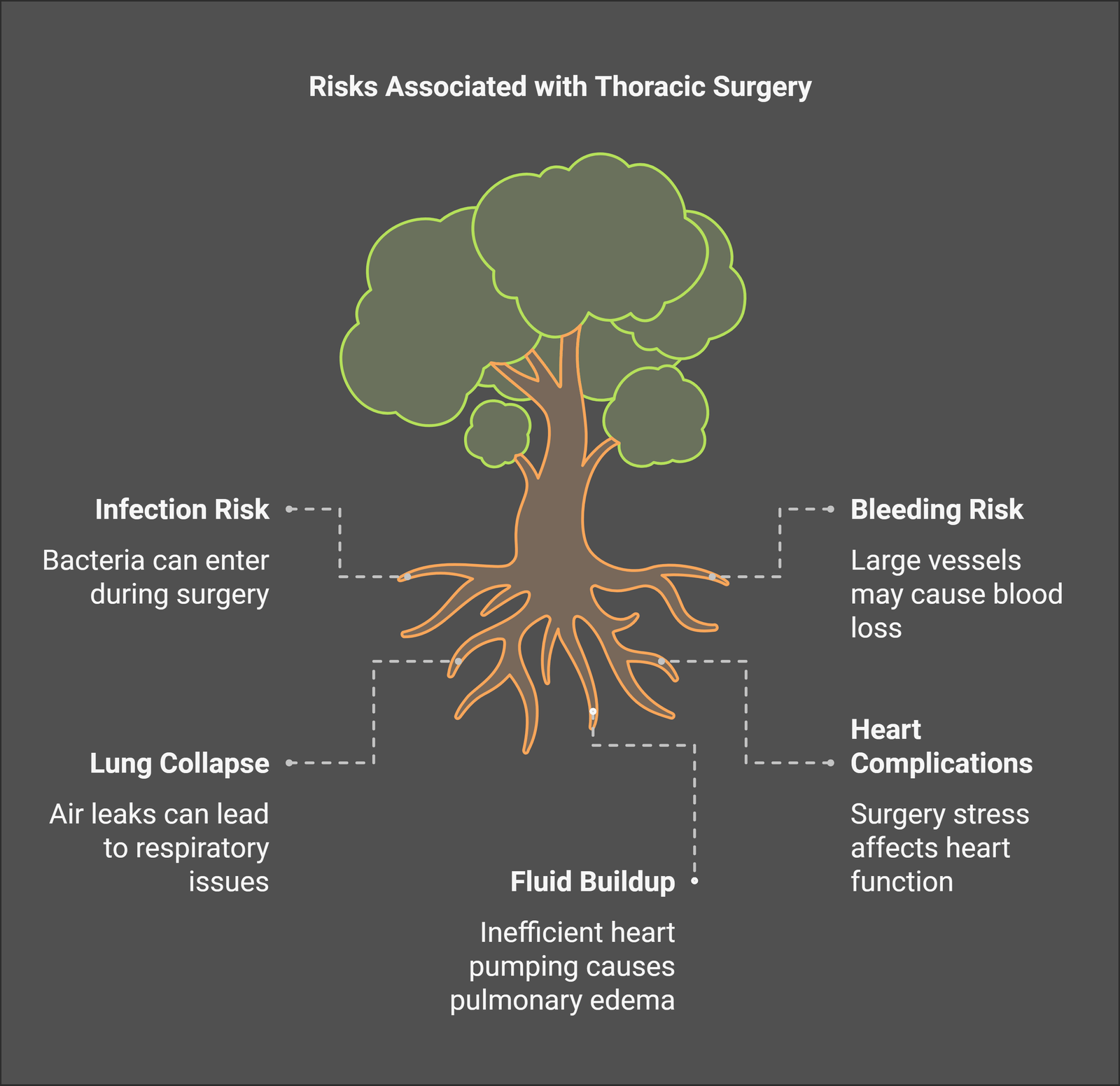
Infection and Bleeding: Thoracic surgery, like any surgical procedure, comes with inherent risks, including the possibility of infection and bleeding. Infection is a concern in surgeries involving opening the chest cavity, where bacteria can enter and cause complications. This risk is mitigated with sterile techniques, antibiotics, and post-operative care. However, surgery patients should be vigilant for signs of infection, such as fever, increased pain, or redness at the incision site. Infections can sometimes delay recovery and require additional medical treatment, including drainage or prolonged antibiotic therapy.
Similarly, bleeding is another risk during thoracic surgery, especially when large blood vessels are involved, such as in heart surgery or aortic repair. Surgeons take great care to minimize blood loss during the procedure. Still, there is always the potential for bleeding after surgery, which can result in the need for transfusions or further surgical intervention. Surgeons monitor patients closely in the recovery phase to detect and manage any signs of bleeding early.
Lung Collapse: Lung collapse (or pneumothorax) is a potential complication, particularly in surgeries involving the lungs or chest wall. When air leaks into the space between the lungs and the chest wall, it can cause the lungs to collapse, which may lead to difficulty breathing and other respiratory complications. In most cases, a pneumothorax can be treated by inserting a chest tube to remove the air and allow the lung to re-expand. However, severe cases may require additional procedures or extended hospital stays. Surgeons in India, as well as globally, take great precautions during surgery to minimize the risk of lung collapse and manage it promptly if it occurs.
Heart Issues: Since thoracic surgery often involves procedures that affect the heart, such as heart valve repair, coronary artery bypass grafting, or surgeries involving the aorta, there are inherent risks to the heart's function during and after surgery. These include arrhythmias (irregular heart rhythms), heart failure, or other cardiovascular complications that may arise due to the stress of surgery on the heart. Sometimes, the heart may need to be temporarily bypassed using a heart-lung machine, which carries additional risks. However, thoracic surgeons carefully monitor heart function during surgery, and patients are generally given medications to help regulate heart rhythm and blood pressure during recovery.
Swelling or Fluid Buildup (Pulmonary Edema): Pulmonary oedema, or fluid accumulation in the lungs, is a serious complication that can occur after thoracic surgery. It may happen when the heart cannot pump blood efficiently after surgery, leading to fluid buildup in the lungs. Symptoms can include shortness of breath, coughing, and fluid retention in the body. Patients undergoing heart or complex lung surgeries may be more prone to this condition. Surgeons take preventive measures, including careful monitoring of fluid intake and output, medications to manage heart function, and respiratory therapy to help clear the lungs. Early detection and treatment of pulmonary oedema are crucial to avoid long-term damage to lung tissue or the heart.
Recovery and Outlook:
Recovery after thoracic surgery is a multi-step process that involves several phases. The specific recovery time and outlook depend on the type of surgery performed, the patient's overall health, and any underlying conditions. Thoracic surgeries can range from minimally invasive procedures to complex open surgeries, each requiring different care strategies. Understanding what to expect during recovery and the long-term outlook is crucial for patients undergoing these surgeries.
The Recovery time depends on the procedure's complexity and the patient's health.
During the first phase of recovery, patients will be closely monitored for complications, such as infections, bleeding, or lung collapse, to ensure prompt intervention.
Proper post-surgery care is vital to achieving a successful recovery after thoracic surgery.
Long-Term Outlook:
The long-term outlook after thoracic surgery depends on several factors, including the type of surgery, the underlying condition being treated, the patient's age, and overall health. While many patients experience significant improvement in their quality of life, the recovery process can continue for several months, especially for more complex surgeries.
Psychological and Emotional Recovery:
It's also important to acknowledge the psychological aspect of recovery. Major surgeries, especially those involving cancer or chronic diseases, can take an emotional toll on patients. Fear, anxiety, and depression are common during the recovery process. Many thoracic surgery centres offer psychological support, including counselling or support groups, to help patients navigate these challenges and adjust to life post-surgery.
The recovery and long-term outlook after thoracic surgery depend on various factors, including the type of procedure, the patient's health condition, and their adherence to post-surgical care and rehabilitation. While recovery may take time, many patients experience significant improvements in their quality of life, whether it's relief from cancer symptoms, better heart function, or improved lung health. Working closely with healthcare providers and following a comprehensive recovery plan is essential to achieving the best possible outcome.
Recognizing early signs of complications after thoracic surgery is crucial to prevent long-term issues and ensure the best possible recovery. While some discomfort is expected after surgery, specific symptoms could indicate a problem that requires immediate attention. It is essential to communicate with your thoracic surgeon or healthcare provider if you experience any of the following:
1. Difficulty Breathing or Chest Pain:
Breathing problems or chest pain after surgery should never be ignored. Difficulty breathing or sharp chest pain may indicate a complication such as pneumothorax (lung collapse), blood clots (pulmonary embolism), or a problem with the heart or lungs, such as fluid buildup (pulmonary oedema). This could also signal an infection or complications at the site of surgery. If you experience persistent difficulty breathing, tightness in the chest, or sudden, severe pain, seek medical attention immediately.
2. Fever or Excessive Coughing:
Fever is a typical response to infection, and excessive coughing could indicate a respiratory issue such as pneumonia or a lung infection. After thoracic surgery, infections are a concern, particularly in the lungs or chest cavity. A fever, especially if accompanied by chills, persistent coughing, or yellow or green sputum, could suggest an infection that requires prompt treatment to prevent it from worsening.
3. Persistent or Worsening Symptoms, Such as Swelling in the Chest Area:
Swelling or fluid retention in the chest or surrounding areas may indicate pleural effusion (fluid buildup in the pleural space) or hemothorax (blood accumulation in the chest cavity). These complications can occur after surgery, and failure to address them could lead to impaired lung function and additional health issues. If you notice increasing discomfort, swelling, or pressure in the chest area, this is a signal that your doctor needs to assess the situation.
4. Signs of Infection Like Redness, Warmth, or Discharge at the Surgery Site:
Infections can develop at the incision site after thoracic surgery, leading to symptoms like redness, swelling, warmth, or pus-like discharge. Infections can delay recovery and, in some cases, become severe or spread to the bloodstream. While some redness and mild swelling are expected in the first few days after surgery, these signs should not worsen or be accompanied by other symptoms such as fever or pain.
5. Unexplained Weight Loss or Loss of Appetite:
In the weeks following thoracic surgery, patients may experience a reduced appetite due to pain or discomfort. However, unexplained weight loss or a significant decrease in appetite, particularly when combined with other symptoms like fatigue, fever, or night sweats, may indicate an underlying issue such as an infection, malnutrition, or a recurrence of cancer.
6. Dizziness, Lightheadedness, or Fainting:
Dizziness or fainting spells can be signs of several conditions, including low blood pressure, anaemia, or complications from anaesthesia. After thoracic surgery, monitoring for issues related to circulation is essential, especially if you're immobilized for some time. Severe dizziness or fainting should be taken seriously.
Following thoracic surgery, you must remain vigilant and contact your healthcare provider promptly if you experience any of these symptoms. Early intervention can help avoid more serious complications, such as spreading infections, blood clots travelling to the lungs (pulmonary embolism), or lung collapse, which can impact recovery and overall health. Thoracic surgeons are trained to assess and address complications early, so never hesitate to seek medical advice if you're unsure about new symptoms.
Thoracic surgery is complex, and recovery requires careful monitoring and management. By keeping your surgeon informed of any concerning symptoms, you play an active role in your recovery, ensuring you're on track for the best possible outcome.
Thoracic surgeons are highly specialized professionals trained to treat various chest-related conditions that affect the lungs, heart, oesophagus, diaphragm, and surrounding structures. Their expertise goes beyond general surgery; they have the skills and knowledge to handle some of the most complex diseases and medical conditions within the chest cavity. Consulting a thoracic surgeon is essential for achieving the best possible outcomes when it comes to conditions like lung cancer, heart disease, and chronic respiratory conditions.
Expertise in Managing Complex Diseases:
Thoracic surgeons are uniquely qualified to perform open and minimally invasive procedures, allowing them to treat conditions ranging from relatively simple issues to advanced, life-threatening diseases. This specialized skill set enables them to perform surgeries precisely and reduce the risks associated with each procedure. Whether you need treatment for esophageal cancer, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), or pulmonary hypertension, a thoracic surgeon can tailor the treatment to your specific needs.
For example, in the case of lung cancer, early intervention through surgery can significantly improve survival rates. Thoracic surgeons can remove tumours from the lungs with precision, using methods like lobectomy (removal of a portion of the lung) or pneumonectomy (removal of an entire lung). These complex surgeries require a high degree of skill and expertise to ensure that healthy tissue is preserved while effectively treating the cancer.
Advanced Surgical Techniques:
One of the defining characteristics of thoracic surgery is its focus on minimally invasive procedures. Techniques like Video-Assisted Thoracic Surgery (VATS) or robotic-assisted surgery have revolutionized the field by allowing surgeons to perform complex procedures with smaller incisions, leading to shorter recovery times, less pain, and fewer complications for the patient.
Minimally invasive surgery is particularly valuable for patients who are at higher risk due to their age, pre-existing conditions, or other factors that might make traditional open surgery riskier. Choosing a thoracic surgeon skilled in advanced techniques ensures a smoother recovery and faster return to daily activities.
Comprehensive Management of Heart Conditions:
Thoracic surgeons play a key role in treating heart conditions like coronary artery disease, valve disorders, and aneurysms. They are highly skilled in performing surgeries like coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG), heart valve repair, and heart valve replacement. These procedures can prevent heart failure, improve blood circulation, and reduce symptoms of heart disease, significantly enhancing the patient's quality of life.
For example, in patients suffering from valvular heart disease, thoracic surgeons can repair or replace damaged valves, restoring proper heart function and preventing complications like stroke or congestive heart failure. Without this surgical expertise, patients with severe heart conditions may experience a rapid decline in health.
Treatment of Chronic Respiratory Conditions:
Thoracic surgeons play a critical role in diagnosing and treating patients suffering from chronic respiratory diseases. When treatments like medication or oxygen therapy fail, conditions such as COPD, emphysema, and pulmonary fibrosis may require surgical intervention. Thoracic surgeons perform lung volume reduction surgery to enhance breathing, improve lung function, and significantly reduce symptoms, boosting overall health.
Thoracic surgeons are also trained to perform tracheal or oesophagal surgeries in severe respiratory distress. These surgeries can help open the airway, allowing the patient to breathe more efficiently and improve their quality of life. Their expertise ensures that complex respiratory surgeries are carried out with precision, reducing the chances of complications and speeding up the recovery process.
Collaborative Care:
Thoracic surgeons work closely with oncologists, pulmonologists, cardiologists, and radiologists to ensure comprehensive patient care. This multidisciplinary approach ensures that all aspects of the patient's condition are considered, from diagnosis to post-operative recovery. For instance, in cases of lung cancer, thoracic surgeons collaborate with oncologists to determine whether surgery is needed alongside chemotherapy or radiation therapy, giving the patient the best chance of survival and recovery.
Additionally, thoracic surgeons provide ongoing care and follow-up to ensure that recovery progresses and that the patient remains healthy after surgery. They monitor for complications and provide early intervention if necessary, ensuring patients have the best chance for long-term health.
Many of the conditions treated by thoracic surgeons, such as lung cancer or heart disease, are most successfully treated when caught early. Thoracic surgeons play a vital role in diagnosing these conditions through screening tests like CT scans, bronchoscopy, or biopsies. Early diagnosis and intervention can lead to significantly better patient outcomes, allowing for less invasive treatment options and a better overall prognosis.
For example, early-stage lung cancer is often treatable with surgery, while late-stage lung cancer may require more aggressive treatments like chemotherapy. By consulting a thoracic surgeon at the first signs of trouble, patients can receive timely treatment that may save their lives and prevent more extensive procedures in the future.
India is home to some of the world's most skilled and experienced thoracic surgeons. With advancements in medical technology and a growing network of world-class hospitals and surgical centres, India provides various high-quality, cost-effective surgical options for patients worldwide. Whether you need lung cancer surgery, heart valve repair, or oesophagal surgery, a thoracic surgeon in India has the expertise to handle complex procedures and deliver excellent outcomes.
India also offers access to cutting-edge technologies such as robotic-assisted surgery and minimally invasive techniques, which are becoming increasingly common in thoracic surgery. The combination of skilled surgeons, modern medical infrastructure, and affordability makes India an attractive destination for thoracic surgery.
Glossary of Terms:
Consulting a thoracic surgeon is essential for patients facing chest-related health issues. These specialized surgeons treat lung cancer, heart disease, and chronic respiratory problems. With advanced surgical techniques, a collaborative care approach, and a focus on early intervention, thoracic surgeons ensure the best possible outcomes for their patients. Whether you're dealing with a serious heart condition, lung cancer, or chronic respiratory issues, thoracic surgeons offer the care and treatment you need for a healthier future.
If you or a loved one are facing respiratory or chest-related challenges, don't wait to seek expert care. Schedule your consultation today and take the first step toward better health and recovery!
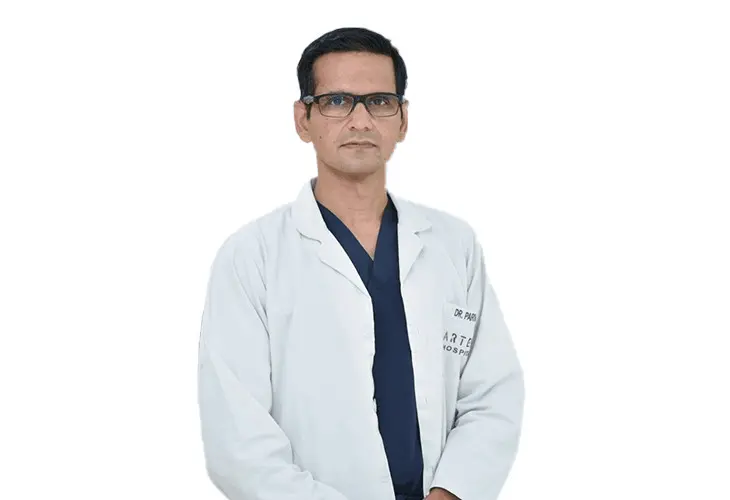

18+ Yrs Exp | 5,700+ Thoracic & Robotic Cancer Surgeries
Dr. Parveen Yadav is a Director and Senior Consultant in Thoracic and Surgical Oncology, specializing in minimally invasive and robotic lung and esophageal surgeries, with advanced training from AIIMS and Tata Memorial Hospital.
View Full Profile Pain After Thoracic Surgery: Tips for Smooth Recovery
Pain After Thoracic Surgery: Tips for Smooth Recovery
 Diet & Lifestyle for Thoracic Cancer Prevention | Dr. Parveen Yadav
Diet & Lifestyle for Thoracic Cancer Prevention | Dr. Parveen Yadav
 Robotic Thoracic Surgery: How Da Vinci Technology is Revolutionizing Chest Procedures
Robotic Thoracic Surgery: How Da Vinci Technology is Revolutionizing Chest Procedures
Struggling with pain after chest surgery? Dr. Parveen Yadav shares expert recovery tips, causes of shoulder pain, PTPS signs, and what your discharge sheet won't tell you.
Discover how diet, breathing exercises & daily habits help prevent and recover from thoracic cancer. Expert insights from Dr. Parveen Yadav, Chest Surgery India
Discover how Da Vinci robotic surgery is transforming chest procedures in Gurgaon. Less pain, faster recovery & expert care by a certified thoracic surgeon
Copyright 2026 © Dr .Parveen Yadav all rights reserved.
Proudly Scaled by Public Media Solution!