

Esophageal cancer is a challenging and often aggressive disease that requires a comprehensive appoach to treatment. Among the key treatment modalities for esophageal cancer are surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy.
In this blog, we will delve into each of these treatment options, their mechanisms, potential benefits, and how they are often combined to provide the best possible outcomes for patients.
Conclusion:
The treatment of esophageal cancer is complex and multifaceted, often involving a combination of surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy. These treatment modalities can be used individually or in combination, depending on the patient's situation. Advances in medical technology and ongoing research continue to improve the effectiveness of esophageal cancer treatments, offering hope for better outcomes and improved quality of life for patients facing this challenging disease.

18+ Yrs Exp | 5,700+ Thoracic & Robotic Cancer Surgeries
Dr. Parveen Yadav is a Director and Senior Consultant in Thoracic and Surgical Oncology, specializing in minimally invasive and robotic lung and esophageal surgeries, with advanced training from AIIMS and Tata Memorial Hospital.
View Full Profile Pain After Thoracic Surgery: Tips for Smooth Recovery
Pain After Thoracic Surgery: Tips for Smooth Recovery
 Diet & Lifestyle for Thoracic Cancer Prevention | Dr. Parveen Yadav
Diet & Lifestyle for Thoracic Cancer Prevention | Dr. Parveen Yadav
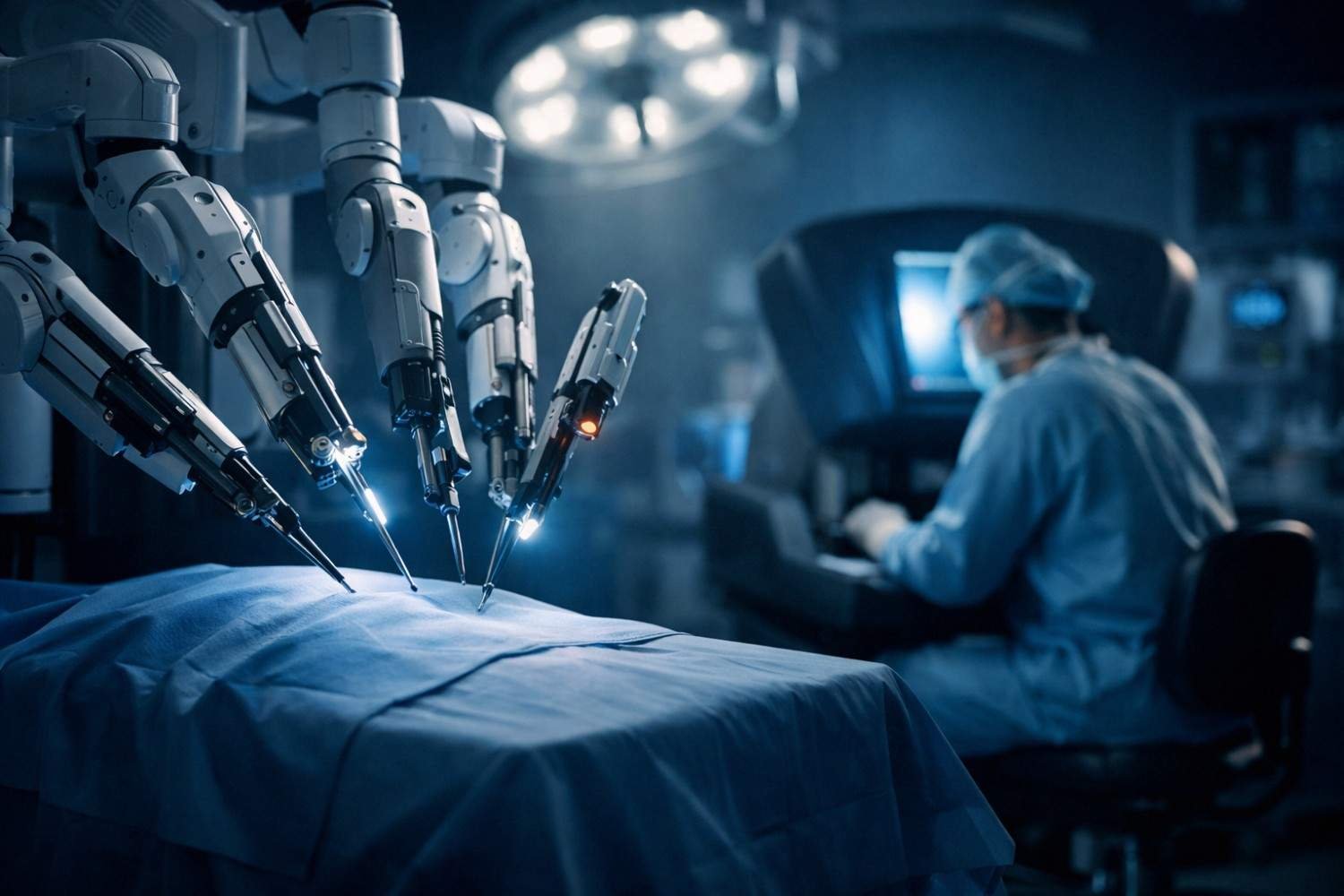 Robotic Thoracic Surgery: How Da Vinci Technology is Revolutionizing Chest Procedures
Robotic Thoracic Surgery: How Da Vinci Technology is Revolutionizing Chest Procedures
Struggling with pain after chest surgery? Dr. Parveen Yadav shares expert recovery tips, causes of shoulder pain, PTPS signs, and what your discharge sheet won't tell you.
Discover how diet, breathing exercises & daily habits help prevent and recover from thoracic cancer. Expert insights from Dr. Parveen Yadav, Chest Surgery India
Discover how Da Vinci robotic surgery is transforming chest procedures in Gurgaon. Less pain, faster recovery & expert care by a certified thoracic surgeon
Copyright 2026 © Dr .Parveen Yadav all rights reserved.
Proudly Scaled by Public Media Solution!