

Understanding medical conditions is crucial for managing health effectively. Empyema and Emphysema are two distinct respiratory conditions that can severely impact a person's life. This blog explains the differences between Empyema and Emphysema, helping you recognize their symptoms, causes, and treatments. While they both affect the lungs, they are distinct in their causes, symptoms, and treatment approaches.
Empyema is a severe condition when pus accumulates in the space between the lung and the chest wall. Common causes include bacterial infections, pneumonia, or lung abscesses. When these infections spread to the pleural space, they trigger an inflammatory response, leading to pus buildup.
Bacterial infections, especially following pneumonia, commonly cause Empyema. Other risk factors include chest surgery, lung abscess, or trauma to the chest. Individuals with compromised immune systems or chronic lung diseases are also at higher risk of developing Empyema.
Also Read: Empyema vs Pneumonia: Differences in Symptoms and Treatment
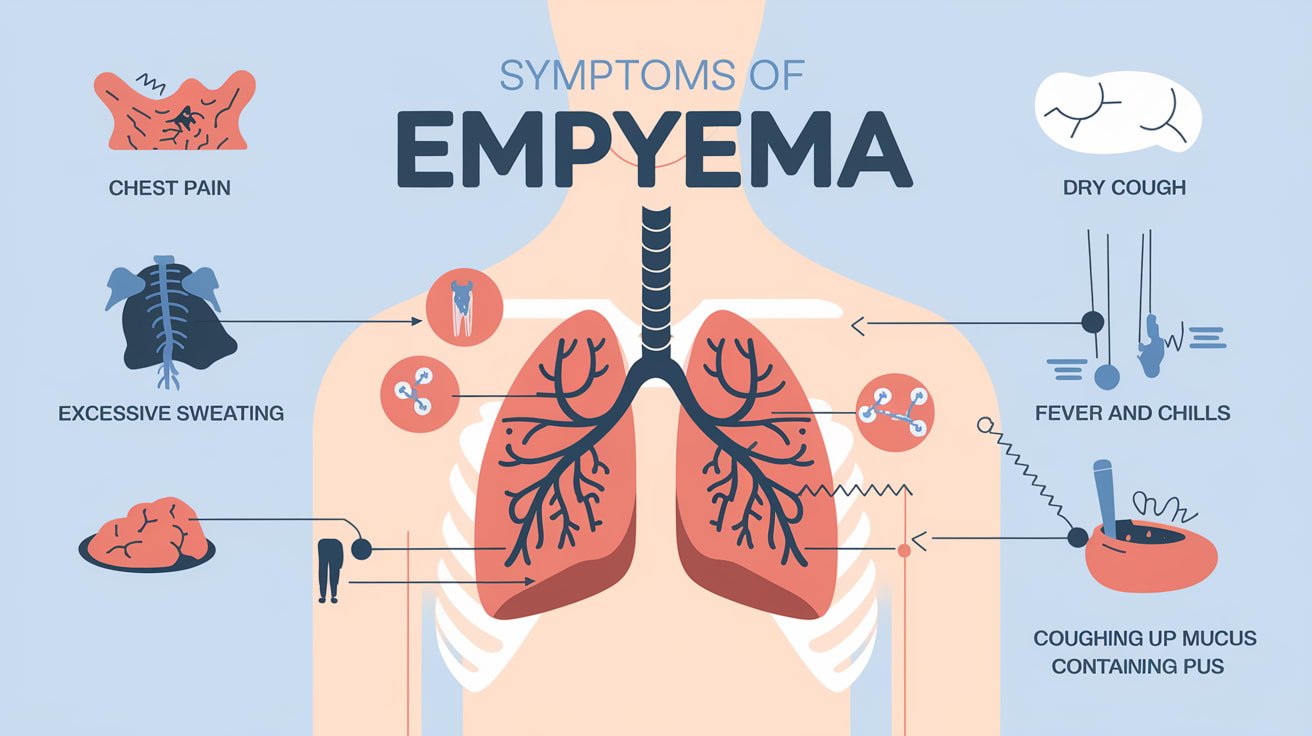
Empyema is the accumulation of pus in the space between the chest wall and the lungs. Symptoms may include:
Chest pain: Patients may experience sharp or stabbing pain in the chest, especially when breathing deeply or coughing.
Fever: A high body temperature is typically accompanied by chills and sweating.
Shortness: Shortness of breath can cause difficulty breathing or breathlessness, especially when exerting or lying flat.
Cough: A persistent cough may sometimes produce foul-smelling or bloody sputum.
Fatigue: Fatigue refers to tiredness or weakness due to infection and inflammation.
Decreased appetite: Loss of appetite and unintentional weight loss can occur.
Malaise: A general feeling of discomfort, unease, or illness.
Cyanosis: Bluish discolouration of the lips or fingernails due to inadequate blood oxygenation.
If you experience these symptoms, you must seek medical attention promptly. Empyema is a severe condition that requires medical intervention, such as antibiotics and drainage of the infected fluid.
Treatment for Empyema typically involves a combination of medical therapies and, in some cases, surgical intervention. Here's an outline of the general approach:
Antibiotics: Empyema is usually treated with antibiotics to target the underlying infection. Antibiotic selection depends on the suspected or identified causative organism and its antibiotic susceptibility. Broad-spectrum antibiotics are often initially prescribed until culture results are available.
Thoracentesis: This procedure involves draining fluid from the pleural space using a needle inserted through the chest wall. It helps to relieve symptoms and aids in diagnosis by allowing analysis of the fluid.
Chest Tube Insertion: In cases of significant fluid accumulation or if the Empyema is not resolving with antibiotics alone, a chest tube may drain the infected fluid continuously. This procedure is typically performed under imaging guidance.
Pleural Decortication: In more severe cases or when complications such as locations (pockets of trapped fluid) or thickened pleura occur, surgery may be necessary to remove the infected tissue and improve lung expansion. This procedure is known as pleural decortication.
Supportive Care: Patients with Empyema may require supportive measures such as supplemental oxygen, pain management, and respiratory therapy to help manage symptoms and promote recovery.
Follow-up: Regular follow-up appointments are crucial to monitoring progress, adjusting treatment as needed, and ensuring complete resolution of the infection.
Empyema is a severe condition that requires timely and appropriate treatment to avoid further complications and ensure quick recovery. The treatment plan may change depending on the majority of the condition, the patient's overall health, and individual factors. Therefore, it is crucial to make treatment decisions after consulting with a healthcare professional.
Severe cases may require surgical intervention, and patients seeking Empyema treatment in Gurgaon, Delhi, can find specialized care at leading hospitals like Chest Surgery India.
Empyema is diagnosed using imaging tests like chest X-rays or CT scans to visualize the fluid collection. A pleural fluid sample may be taken (thoracentesis) to identify the infection and determine the best treatment approach.
Emphysema is a chronic respiratory disease that develops over time due to prolonged exposure to irritants, such as cigarette smoke. This damage results in decreased lung function and difficulty breathing.
The primary cause of Emphysema is long-term exposure to airborne irritants, especially cigarette smoke. Other factors include air pollution, chemical fumes, and genetic predisposition. A rare genetic condition called alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency can also lead to Emphysema.
Emphysema is a lung condition that primarily affects the air sacs (alveoli) in the lungs. Symptoms of Emphysema often develop gradually over time and may include:
1. Shortness of breath, especially during physical exertion
2. Wheezing
3. Chronic cough, often with mucus production (sometimes called "smoker's cough")
4. Fatigue
5. Reduced exercise tolerance
6. Chest tightness
7. Difficulty breathing, mainly when lying down
8. Barrel chest (a rounded, bulging chest shape)
9. Weight loss (in advanced stages)
10. Bluish or greyish lips or fingernail beds (indicating low oxygen levels)
It is essential to note that the symptoms of Emphysema can vary in severity and may deteriorate over time if left untreated. If you or someone you know is experiencing these symptoms, it's essential to consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and management.
Emphysema is diagnosed through lung function tests (spirometry) to measure lung capacity and efficiency. Imaging studies such as chest X-rays and CT scans help visualize the extent of lung damage. A thorough medical history and physical examination are also crucial for an accurate diagnosis.
Management of Emphysema typically involves a combination of lifestyle changes, medication, pulmonary rehabilitation, and sometimes surgical interventions. Here's an overview:
Smoking Cessation: The most crucial step in managing Emphysema is to quit smoking. This slows down the progression of the disease and reduces lung damage.
Bronchodilators: These medications help relax the muscles surrounding the air passages, easing breathing. They come in short-acting and long-acting forms.
Inhaled Corticosteroids: These medications help reduce inflammation in the airways.
Antibiotics: Sometimes prescribed to treat respiratory infections that can worsen emphysema symptoms.
Oxygen Therapy: Patients with severe Emphysema may require supplemental oxygen to increase their blood oxygen levels.
Pulmonary Rehabilitation: This involves a structured program of exercise, education, and support to help improve lung function, increase exercise tolerance, and enhance quality of life.
Exercise: Regular physical activity can strengthen respiratory muscles and improve overall fitness.
Healthy Diet: Eating a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins daily is crucial for maintaining good health.
Avoiding Environmental Irritants: Minimizing exposure to air pollution, dust, and other irritants can help reduce symptoms.
Vaccinations: To reduce the risk of respiratory infections, patients with Emphysema should receive annual flu shots and pneumococcal vaccines.
Lung Volume Reduction Surgery (LVRS) removes damaged lung tissue, improving lung function and alleviating symptoms.
Lung Transplantation: For severe cases of Emphysema where other treatments have failed, lung transplantation may be considered.
Regular Monitoring: Patients with Emphysema need regular check-ups to monitor their condition, adjust medications, and address new symptoms or concerns.
The main goal of managing Emphysema is to reduce symptoms, improve quality of life, and slow disease progression. This can be achieved through a combination of medical treatments and lifestyle modifications. Patients must work closely with their healthcare team to create an effective treatment plan.
Empyema involves the accumulation of pus in the pleural space due to infection, whereas Emphysema is damage to the lung's air sacs, primarily due to smoking.
Empyema is caused by infections and physical trauma to the chest, while Emphysema is mainly due to long-term exposure to harmful airborne substances. Empyema can develop quickly following an infection, while Emphysema develops gradually over years of irritant exposure.
Empyema symptoms include chest pain, fever, and difficulty breathing, while emphysema symptoms are more related to breathing difficulties and chronic coughing. Empyema often presents with signs of infection, whereas emphysema symptoms are primarily due to lung damage and reduced airflow.
Empyema is diagnosed through imaging tests and pleural fluid analysis, while Emphysema is diagnosed through lung function tests and imaging studies. Empyema may also require laboratory tests to identify the bacteria causing the infection.
Empyema treatment focuses on eliminating the infection and draining pus, whereas emphysema treatment aims at managing symptoms and preventing further lung damage. Empyema treatment is typically more urgent and may involve invasive procedures, while emphysema management focuses on long-term lifestyle changes and medications.

Empyema can cause significant discomfort and breathing difficulties, leading to hospitalizations and a prolonged recovery period. The condition can severely impact a person's ability to perform daily activities and may require extended periods of rest and medical care.
Emphysema leads to chronic breathing problems, limiting physical activities and reducing the overall quality of life. Patients often require long-term medical management and may need to use supplemental oxygen. The progressive nature of Emphysema can lead to increasing dependence on healthcare services and support.
Empyema, if treated promptly, has a good prognosis. Emphysema, however, is a progressive disease with a more challenging prognosis, often requiring ongoing medical support. Early diagnosis and adherence to treatment plans can improve outcomes for both conditions.

Preventing Empyema involves treating respiratory infections promptly and maintaining good hygiene to avoid infections. Vaccinations against pneumonia and influenza can also help reduce the risk of Empyema.
Preventing Emphysema includes avoiding smoking and reducing exposure to airborne pollutants and chemicals. Using protective equipment in environments with harmful fumes and maintaining good indoor air quality are also necessary preventive measures.
Managing both conditions effectively requires regular medical check-ups, a healthy lifestyle, and adherence to prescribed treatments. For Empyema, following the entire course of antibiotics and keeping follow-up appointments is crucial. For Emphysema, quitting smoking, staying active, and participating in pulmonary rehabilitation can significantly improve quality of life.
Consider a patient who presents with fever, chest pain, and a productive cough. Imaging reveals pleural effusion, and thoracentesis confirms the diagnosis of Empyema. Prompt antibiotic therapy and drainage procedures resolve symptoms and lead to successful recovery.
In contrast, another patient with a history of smoking presents with exertional dyspnea and chronic cough. Pulmonary function tests demonstrate reduced lung capacity, and imaging reveals characteristic signs of Emphysema. The patient undergoes pulmonary rehabilitation and receives bronchodilators for symptom management.
In conclusion, understanding the disparities in Empyema vs Emphysema is crucial for accurate diagnosis and effective management. Identifying these conditions enables healthcare providers to tailor treatment plans to individual patient needs, improving outcomes and quality of life. For expert care and guidance regarding respiratory conditions, consult Dr Parveen Yadav at Chest Surgery India, the best Empyema treatment hospital in Gurgaon, Delhi. If you're looking for an Empyema treatment specialist in Delhi, you can trust Dr Yadav and his team's expertise and dedication.
1. What are the main differences between Empyema and Emphysema?
Empyema is an infection in the pleural space, while Emphysema is a chronic lung condition affecting the alveoli.
2. What are the main symptoms of Empyema?
Ans: The main symptoms of Empyema include fever, chest pain, shortness of breath, and coughing up blood-streaked sputum.
3. What causes Emphysema?
Ans: It is a chronic lung disease that is mainly caused by prolonged exposure to irritants, with the most common one being cigarette smoke.
4. How is Empyema diagnosed?
Ans: Diagnosis of Empyema often involves imaging tests such as chest X-rays or CT scans, along with laboratory analysis of pleural fluid obtained through thoracentesis.
5. What treatment options are available for Emphysema?
Ans: Treatment for Emphysema may include medications such as bronchodilators or steroids, pulmonary rehabilitation programs, and supplemental oxygen therapy. In advanced cases, If a person is suffering from severe lung disease, they may need to consider lung transplantation or lung volume reduction surgery as a treatment option.
6. Can Emphysema be cured?
Ans: While Emphysema cannot be cured, proper management can help alleviate symptoms and slow disease progression, improving the quality of life for affected individuals.
About Dr. Parveen Yadav
Dr. Parveen Yadav is a highly recommended surgeon or specialist for lung cancer treatment in Gurgaon, Delhi. He specialises in minimally invasive and robotic thoracic onco surgery. He has been recognised for 17+ years as the best chest surgeon in India for his expertise in treating chest-related (Chest Surgery) ailments, such as Esophageal (Food Pipe Cancer), Lung, Tracheal (Throat), Chest wall tumours, Mediastinal Tumours, Empyema, and Bronchopleural Fistula cancer. With a focus on precision and innovation, he is dedicated to offering exceptional care to his patients, utilising techniques to ensure optimal outcomes.

18+ Yrs Exp | 5,700+ Thoracic & Robotic Cancer Surgeries
Dr. Parveen Yadav is a Director and Senior Consultant in Thoracic and Surgical Oncology, specializing in minimally invasive and robotic lung and esophageal surgeries, with advanced training from AIIMS and Tata Memorial Hospital.
View Full Profile Pain After Thoracic Surgery: Tips for Smooth Recovery
Pain After Thoracic Surgery: Tips for Smooth Recovery
 Diet & Lifestyle for Thoracic Cancer Prevention | Dr. Parveen Yadav
Diet & Lifestyle for Thoracic Cancer Prevention | Dr. Parveen Yadav
 Robotic Thoracic Surgery: How Da Vinci Technology is Revolutionizing Chest Procedures
Robotic Thoracic Surgery: How Da Vinci Technology is Revolutionizing Chest Procedures
Struggling with pain after chest surgery? Dr. Parveen Yadav shares expert recovery tips, causes of shoulder pain, PTPS signs, and what your discharge sheet won't tell you.
Discover how diet, breathing exercises & daily habits help prevent and recover from thoracic cancer. Expert insights from Dr. Parveen Yadav, Chest Surgery India
Discover how Da Vinci robotic surgery is transforming chest procedures in Gurgaon. Less pain, faster recovery & expert care by a certified thoracic surgeon
Copyright 2026 © Dr .Parveen Yadav all rights reserved.
Proudly Scaled by Public Media Solution!